What Is A Car Alternator And How Does It Work?
Everything You Need to Know About Car Alternators
Find your tyre
READ THE DIMENSIONS OF TYRES

In the UAE, the car is no more than a means of transportation. It is a lifeline for daily commuting, family trips, and business. For this reason, keeping your engine and electrical systems in shape is crucial. One important component in the electrical system is the alternator, which many tend to overlook.
This article digs deep into the question: what is a car alternator, and how does it work? We'll also explore how it works in the toughest climatic conditions of the UAE and give helpful tips to car owners in that region.
What is a Car Alternator?
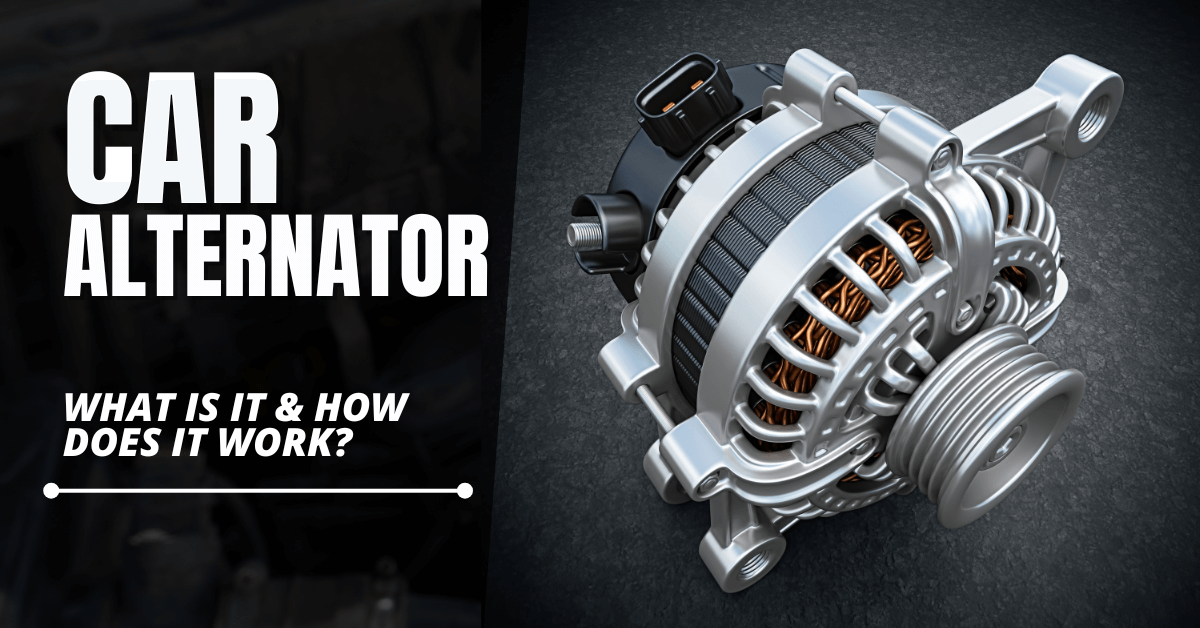
A car alternator is an essential part of a vehicle's electrical system that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy while the engine is running. It works to charge the battery and power the electrical systems in the car, for example, headlights, air conditioning, and the onboard audio system. While commonly referred to as a car dynamo, they are not the same in their operation.
While in older vehicles, a dynamo may have been used, their working principles are distinct. Modern-generation vehicles in the UAE have taken to using alternators because they provide efficient operation, durability, and the generation of more power.
In the UAE, where summer temperatures can reach as high as 55 degrees, the alternator must work hard to keep powering the electrical system and it must withstand that heat. This makes proper alternator care paramount for car owners in the UAE.
Key Components Of a Car Alternator
To understand the workings of an alternator, knowing about certain key components helps understand how an alternator works. These include:
- Rotor: It generates the magnetic field and is connected to the engine through a belt. Inside the alternator, it spins freely.
- Stator: It is firstly located around the rotor and consists of copper wire coils. The rotor creates a magnetic field, which triggers an electrical current in the stator.
- Rectifier: The alternator produces alternating current (AC), while direct current (DC) is used for operating electrical systems within a vehicle. The ACC equivalent is converted into DC through the rectifier, allowing the battery and car systems to receive the necessary power.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator maintains the alternator's voltage at 13.8-14.4V so that the battery receives a steady and proper direct current voltage. This prevents overcharging and undercharging.
- Cooling Fan: The alternator produces a lot of heat. The cooling fan inside it will keep the operating temperature low and prevent overheating, especially in extremely hot summer months as experienced in the UAE.
- Drive Belt: The drive belt or serpent belt drives the alternator and can be connected to the crankshaft of the engine. This belt transmits mechanical energy to the alternator, enabling it to convert the energy into electrical power.
For professional alternator inspection and servicing, visit TyrePlus UAE to ensure your vehicle stays in top condition.
How does the car alternator work
The functioning of a car alternator is that it generates alternating current, which is then converted into direct current for charging the battery and powering electrical systems. The following are the stages of operation of the alternator:
- Transmission of energy: When the car starts, the engine begins to turn the crankshaft. The crankshaft drives the alternator through the drive belt and makes the rotor spin inside the alternator.
- Generation of magnetic field: The spinning rotor causes the creation of a magnetic field around the stator. The magnetic field is instrumental in enabling the generation of electricity.
- Electricity Generation: Due to the rotation of the rotor, an electric current is induced in the copper windings of the stator. The induced current is an alternating current.
- Rectification: Because the car runs on direct current, the AC generated from the alternator is directed to the rectifier, which converts it to DC supply. This is then supplied to both the battery and electrical systems.
- Voltage Regulation: The voltage regulator keeps an eye on the output from the alternator to make sure it remains within the right levels. If the voltage gets too high, the regulator protects the electrical systems from damage. Otherwise, if it is too low, the regulator kicks in to make sure that the battery is charged properly.
- Distribution of current: The current generated from the alternator is supplied to the battery for recharging and to various electrical systems such as lights, air conditioning, infotainment systems, and others.
The Role of the Car Alternator in Your Vehicle’s Electrical System
The alternator is crucial because it supplies power to the electrical systems of the vehicle while keeping the battery charged. Should the alternator develop faults, it may cause problems such as:
- Battery Drain: When the alternator is not charging the battery, the battery will eventually drain and shut down, leaving the driver stranded.
- Power Failures: If your alternator malfunctions, electrical systems in your car, such as headlights, dashboard pot lights, and air conditioning, will not work, causing failure or problems.
- Engine Stalling: A weak alternator fails to supply the power necessary for the work of critical engine components like an AC compressor and may thus cause the engine to stall.
Due to the scorching conditions in the UAE, where heat and humidity are some of the many concerns regarding the operation of an alternator, proper care, and frequent checks are important for the reliable service of the alternator.
Signs of a Failing Alternator
Understanding when an alternator has given up is vital in preventing a possible breakdown, especially in the extreme weather environment as is in the UAE. Here are some of the signals of an aging alternator:
- Dim Lights and Flickering: If your car's lights start dimming or flickering, mainly while idling or during low-speed driving, this might indicate that the alternator is failing to charge the lights sufficiently.
- Handling Warning Lights: Most modern vehicles come with an alternator or battery warning light displayed on the dashboard. If this light comes on, it indicates a fault with the alternator or charging system.
- Dead Battery: A bad alternator can cause the battery to die from lack of proper charging. If you are suddenly faced with a dead battery, that could indicate alternator failure.
- Electrical Failures: If you notice that electrical components, such as power windows, air conditioning, or radio, are not functioning, that may indicate alternator failure.
- Strange Noises: A failing alternator may make a whining or grinding noise and could well indicate worn bearings or internal other damages.
- Stalling Engine: When such power is no longer fed to the engine, the dropping engine could easily stall. In case it becomes a frequent occurrence, this is a serious issue.
Importance of Alternator Maintenance in UAE
Due to the extremely high desert conditions, alternate electrical systems endure severe strains in the UAE. Heat and dust lead to fatigue and, therefore, to the necessity of frequent alternator maintenance. The signs indicating alternator malfunction are dimming of lights, starting difficulty, and strange sounds emanating from the engine region.
To keep your Alternator in the best condition, consider regular car maintenance from TirePlus, trusted automotive experts. Access checks on the battery and electrical car system should always take place so that small yet critical problems can be diagnosed early to prevent breakdowns.
How to Take Care of Your Car Alternator
Maintenance should essentially cover sources of hassle that ought to take care of the longevity of the alternator. Here are a few steps to take care of their alternator:
- Check the Drive Belt Regularly: The alternator is driven by a serpentine belt. Ensure it is in good condition and correctly tensioned. A loose or worn-out belt can lead to poor alternator performance.
- Inspect the Alternator: Have your alternator checked regularly. A worn-out alternator will be evident. Test the output for proper voltage.
- Protect Your Battery If the starter is weak or damaged, the alternator will be under extra stress. Always clean the battery terminals to prevent corrosion and ensure good electrical contact.
- Don't forget the UAE temperatures: Extreme heat can stress the alternator and all engine components. Try to park your car under shade, if possible, to keep it from overheating, and check your cooling system from time to time.
- Replace a Failing Alternator: If your alternator is over 7-10 years old and there's some indication it's not functioning well, have it replaced now to prevent an unexpected failure in the harsh UAE heat.
Conclusion
In the UAE, where temperatures regularly exceed 40 degrees C, the alternator is an important part of the vehicle's electrical system. It assures that the battery will stay charged and all electric components—from air conditioning to headlights—are all working properly. Regular check-ups and awareness of the signs of failing alternators are vital to avoid breakdowns in desert heat.
If you notice any sign of alternators that are dimming lights, electrical failures, or a warning on the dashboard, an immediate inspection is required to prevent further damage and consequent repairs that could cost you. With insight into a car alternator's functioning, UAE car owners can ensure their vehicle remains in the best of conditions even in desert climate challenges.
